算法一般出现在笔试环节 大厂在面试环节也会让你写伪代码或者口头讲述实现逻辑
准备一些经典的数据结构算法是很有必要的 当然尽量能在工作的时候思考一下每一种类型的数据结构操作方法
- 栈、队列、链表
- 有序,相连的
- 集合、字典
- 无序的池子
- 树、堆、图
- 特殊条件相连的
栈stack-后进先出
// [].pop() 删除最后一项并返回
const stack = [];
stack.push(1); // 数组最右侧(后)新增一项 -进栈
stack.push(2); // [1,2]
const item1 = stack.pop(); // [1] 删除数组最右侧(后)项-出栈
const item2 = stack.pop();class Stack {
constructor() {
this.stack = []
}
// 进栈
push(item) {
this.stack.push(item)
}
// 出栈
pop() {
this.stack.pop()
}
// 查看栈的最后一项
peek() {
return this.stack[this.getCount() - 1]
}
// 查看栈内数量
getCount() {
return this.stack.length
}
// 判断栈是否清空
isEmpty() {
return this.getCount() === 0
}
}10进制转二进制
数字除2取余数的每个余数倒序输出 也就是除2之后入栈,再出栈输出结果
函数调用栈
指的是嵌套调用函数,开始执行和执行结束的顺序 后执行的函数,先执行结束
不是事件队列,调用栈是同步函数执行,事件队列是异步函数存储池子,是先进先出的
有效括号校验
多种括号闭合,并且{(})要正确闭合
收集所有不同字符串括号到数组,数组长度相同则闭合。
有效-括号位置要对应上,左括号在第1,右括号要在最后
入栈时存数组index,对应的右括号要是,(length-1)-index
遍历左括号,跟右括号数组匹配index
- 遍历一次收集括号
- 遍历左括号匹配右括号index,多次
👆 不使用栈的思想,是普通的集合
遍历收集不同的左括号,遇到右括号,出栈对应的左括号,出栈只能出最上面的,即不对应就不出,不需要知道对应的左括号在哪
const a = '\{\{\(\}\}'
const arr = a.split()
const left = ['{','('];
const right = ['}',')'];
const map = new Map([
['}','{'],
[')','('],
]);
const stack = [];
// 奇数字符串不可能闭合 除2有没有余数 不为0就是奇数
if(arr.length%2) {
console.log('非有效括号')
return
}
for(let i = 0; i<arr.length; i++){
const item = arr[i]
if(left.includes(item)){
stack.push(item)
}else if(map.get(item) === stack[stack.length-1]){
stack.pop()
}
}
if(stack.length) {
console.log('非有效括号')
return
}
console.log('是有效括号')🤔 什么时候考虑栈
- 遍历一次解决问题
- 不一定要每一项都遍历处理时
- 栈可以给的状态:栈的空状态,栈顶元素(栈的最后一项)
队列queue-先进先出
// [].shift() 删除第一项并返回
const queue = [];
stack.push(1); // 入队
stack.push(2); // [1,2]
const item1 = stack.shift(); // [2]出队
const item2 = stack.shift();- 单链队列在出队操作的时候需要 O(n) 的时间复杂度(TODO: 🤔 因为shift删除第一项需要遍历所有项?)
- 循环队列的出队操作平均是 O(1) 的时间复杂度
👇 单链队列
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.queue = []
}
// 入队
enQueue(item) {
this.queue.push(item)
}
// 出队
deQueue() {
return this.queue.shift()
}
// 队列第一项
getHeader() {
return this.queue[0]
}
// 队列长度
getLength() {
return this.queue.length
}
// 判断队列清空
isEmpty() {
return this.getLength() === 0
}
}👇 循环队列
class SqQueue {
constructor(length) {
this.queue = new Array(length + 1)
// 队头
this.first = 0
// 队尾
this.last = 0
// 当前队列大小
this.size = 0
}
enQueue(item) {
// 判断队尾 + 1 是否为队头
// 如果是就代表需要扩容数组
// % this.queue.length 是为了防止数组越界
if (this.first === (this.last + 1) % this.queue.length) {
this.resize(this.getLength() * 2 + 1)
}
this.queue[this.last] = item
this.size++
this.last = (this.last + 1) % this.queue.length
}
deQueue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw Error('Queue is empty')
}
let r = this.queue[this.first]
this.queue[this.first] = null
this.first = (this.first + 1) % this.queue.length
this.size--
// 判断当前队列大小是否过小
// 为了保证不浪费空间,在队列空间等于总长度四分之一时
// 且不为 2 时缩小总长度为当前的一半
if (this.size === this.getLength() / 4 && this.getLength() / 2 !== 0) {
this.resize(this.getLength() / 2)
}
return r
}
getHeader() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
throw Error('Queue is empty')
}
return this.queue[this.first]
}
getLength() {
return this.queue.length - 1
}
isEmpty() {
return this.first === this.last
}
resize(length) {
let q = new Array(length)
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
q[i] = this.queue[(i + this.first) % this.queue.length]
}
this.queue = q
this.first = 0
this.last = this.size
}
}异步函数的事件队列
计算最近请求次数
axios链式调用时,调用一个删除一个shift
忘了具体
双端队列
既可以先入先出也可以先入后出
链表linkedList
链表是一个线性结构,同时也是一个天然的递归结构。 链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。 但是链表失去了数组随机读取的优点 同时链表由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大
const a = { val:'a' };
const b = { val:'b' };
const c = { val:'c' };
a.next = b;
b.next = c;
let pointer = a; // 指针-从a开始
while(pointer.next) {
console.log('处理当前项', pointer.val)
pointer = pointer.next; // 移动指针
}
// 查(取)
// 增 ab之间插入d
const d = { val:'d' };
a.next = d; // 改变一项就会使原链表断掉
d.next = b; // 把断掉的链表接回来
// 删 a后面的d
a.next = b
// 这里的增删都是在已知所有项的时候来手动操作的,当链表项由参数传入,链表处理只知道下一项,不知道上一项和下下一项,怎么操作class Node {
constructor(v, next) {
this.value = v
this.next = next
}
}
class LinkList {
constructor() {
// 链表长度
this.size = 0
// 虚拟头部
this.dummyNode = new Node(null, null)
}
find(header, index, currentIndex) {
if (index === currentIndex) return header
return this.find(header.next, index, currentIndex + 1)
}
addNode(v, index) {
this.checkIndex(index)
// 当往链表末尾插入时,prev.next 为空
// 其他情况时,因为要插入节点,所以插入的节点
// 的 next 应该是 prev.next
// 然后设置 prev.next 为插入的节点
let prev = this.find(this.dummyNode, index, 0)
prev.next = new Node(v, prev.next)
this.size++
return prev.next
}
insertNode(v, index) {
return this.addNode(v, index)
}
addToFirst(v) {
return this.addNode(v, 0)
}
addToLast(v) {
return this.addNode(v, this.size)
}
removeNode(index, isLast) {
this.checkIndex(index)
index = isLast ? index - 1 : index
let prev = this.find(this.dummyNode, index, 0)
let node = prev.next
prev.next = node.next
node.next = null
this.size--
return node
}
removeFirstNode() {
return this.removeNode(0)
}
removeLastNode() {
return this.removeNode(this.size, true)
}
checkIndex(index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size) throw Error('Index error')
}
getNode(index) {
this.checkIndex(index)
if (this.isEmpty()) return
return this.find(this.dummyNode, index, 0).next
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0
}
getSize() {
return this.size
}
}双向链表也就是多一个向前的指针而已如pre
什么时候考虑链表
- 遍历所有项
- 不在意项的位置,有自己的顺序实现
- 操作(增删)项时不希望被数组的顺序束缚(为什么不用数组)
链表和数组
数组
- 优点 - 高效的随机访问能力,有下标就能读取到
- 缺点 - 增删触发其他项移动,这里移动有遍历操作的损耗的 - (删除项如果不需要移动顺序的话,可以把最后一项放到删除项那里,这样其他项其实是不需要变动的。这样删除项损耗最小,但是顺序就乱掉了)
数组适合读 链表适合写
删除链表指定节点
1->2->3->4,要求删除指定的节点(参数) 按照next来遍历while
找到要删除的节点,让上一节点next指向下一节点
问题:没办法拿到上一项
function remove(val) {
// 链表的遍历是next
let pointer = a; // 指针-从a开始
while(pointer.next) {
if(pointer.val === val) {
// 找到了要删除的节点
// 让上一项指向下一项(没办法拿到上一项
per.next = pointer.next;
}
console.log('处理当前项', pointer.val)
pointer = pointer.next; // 移动指针
}
}换种思路,把要删除项的值变成下一项,指针为下下一项
1->2->3->4 1->3->3->4 1->3------>4 3->4
function remove(val) {
// 链表的遍历是next
let pointer = a; // 指针-从a开始
while(pointer.next) {
if(pointer.val === val) {
// 找到了要删除的节点
// 当前项变成下一项 指针指向下下项
pointer.val = pointer.next.val
pointer.next = pointer.next.next
}
pointer = pointer.next; // 移动指针
}
}删除有序数字链表中的重复元素
有序数字所以都是按顺序的,重复会相邻如 123有序,重复只能相邻
判断当前项和下一项的值相同就删除(下一项指向下下项)下一项
链表反转
反转2个节点 当前项的值变成下一项,next指向上一下项(不知道上一项 双指针遍历链表 一个指针从第一项开始 一个指针从第二项开始 1 2 3 4 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ null 1 2 3 4
第二个指针的值只用来暂存 给第一个指针来指 4 3 2 1
let pointer1 = a; // 指针-从a开始
let pointer2 = null; // 先不开始 落后一个
while(pointer1.next) {
console.log('指针1的值', pointer1.val)
console.log('指针2的值', pointer2 && pointer2.val)
const temp = pointer1.next; // 给移动指针做标识下一项
pointer1.next = pointer2; // 第一个指针指向第二个(前一项)
pointer2 = pointer1; // 移动指针2
pointer1 = temp; // 移动指针1
}用落后的指针来获得前一项
多位数转为链表求和
123 + 789 3+9 2+8 1+7 再倒序拼接
判断是否有环形链表
用多个落后的指针来遍历,当落后的项跟当前项相同证明后面的链到前面的
多指针的作用来获取前面的项
原型链
原型链的数据结构就是链表 proto 就是 next
实现一个instanceOf
instanceOf(A,B) {
const pointer = A;
while(pointer) {
if(p===B.prototype) {
return true
}
pointer = pointer._proro_
}
return false
}
instanceOf([], Array)判断第一个参数原型链上是否含有第二个参数 第一个参数是完整的链表,第二个参数是一项 且第一个参数就链表头,遍历指针的值是否等于第二个参数的原型,等于则有
json
json对象是链表,指针从外往里指,path的每一项就是指针,forEach就移动指针
const json = {
a:{b:{c:'json.a.b.c'}},
d:{e:'json.d.e'}
}
const path = ['a','b','c'];
// 根据path的数组层级取到json对象深层数据
path.forEach(item=>{
// json对象是链表,指针从外往里指,path的每一项就是指针,forEach就移动指针
const pointer = json;
pointer = pointer[item];
})不太像链表吧,next都不明显,虽然从外往里遍历来指向是链表的特征,next就是子项 这么说所有的 xx.xx.xx 都是链表了
字典
字典的重点是创建出有效的字典。(字典查找根据key直接得值)
以key value形式存储的数据 ES6 的Map Map是映射的意思,更好的解释字典这种数据结构
无重复字符的最长子串
用指针,这里的指针不是链表的指针 链表指针内嵌下一项,这里只是数组下标取下一项而已,是下标index,并且指针完全由自己控制,想怎么走怎么走
指针作用:扫描字符存入字典
用两个指针,左指针做标记,右指针循环存入字典
两个指针都在开头,第二个指针往右移动,移动发现值跟前面的相同,则第一个指针往右移动,这里不是左指针+1,而是左指针移动到重复项那里(节省不必要的循环
// 找出字符串中无重复字符的字符串的长度
// 如下会有很多无重复字符串,但是要找出长度最长的,所以用到了Math.max
(()=>{
const str = 'qasdxas' // aabcdea->abcde
let pointer1 = 0 // 左指针
let length = 0 // 没有重复字符的长度(左指针到右边的数量
const dict = new Map()
for(let i=0; i<str.length ;i++){
const item = str[i];
// i是右指针 区间是左到右
if(dict.has(item)&& dict.get(item)>=pointer1) {
// 字典中有值且不在左指针区域内,证明重复 移动左指针到左边重复项的后一位
pointer1 = dict.get(item)+1
// dict.clear()
// 清空不可行,存入字典依赖右指针,清空会导致右指针过了的项无法判断重复
// 如上a重复,清空右指针之前的字典,右指针到s时会不知道s已经重复
// 如果要清空,应该清空左指针前的字典(不好操作
// 因此判断重复同时判断重复的项在左指针前(包含左指针)都当重复,是最方便的
}
dict.set(item, i);
length = Math.max(length, i - pointer1 + 1)
}
console.log(length)
})()🤔 有key value的都可以考虑字典的数据结构,感觉什么场景都可以用吧。。。
TODO: 最小覆盖子串
用栈队列作为字典不也行? 操作出栈入栈
指针在算法里面无敌了吧。。。字典都要靠指针来创建
2个数组的交集
跟Set的方法不同 这里用字典思想 创建字典:遍历第一个数组,以key为数组项,值为true或随便,进行存储,就做好了去重 匹配字典:再遍历第二个数组,判断是否在字典里面,再则取出来,并且删除字典项,去重
function test(arr1, arr2) {
const dict = new Map();
let res = [];
// 创建字典
arr1.forEach(item=>{
dict.set(item, true)
})
// 匹配字典
arr2.forEach(item=>{
if(dict.get(item)) {
res.push(item);
dict.delete(item)
}
})
return res;
}找出数组项中2个相加等于目标值的下标
遍历数组判断字典中有没有等目标值-当前项的值,有则匹配成功,没有则存入字典 字典key为数组项,value为下标
const arr = [11,1,2,7]
const target = 9
const dict = new Map();
const res = [];
for(let i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
const item = arr[i]; // 当前项的值
const otherItem = target - item // 期望匹配的值
if(dict.get(otherItem)>-1) { // 判断字典有没有期望值
res.push(i); // 有则返回当前项和字典项下标
res.push(dict.get(otherItem));
break;
} else {
dict.set(ite,i); // 字典没有则当前项存入字典
}
}
console.log(res)树
分层、一对多的数据结构、DOM树、级联选择器、树形数据
深度优先遍历-递归
(()=>{
const tree ={
val:'a',
children:[{
val:'b',
children:[{val:'d',children:[]}, {val:'e',children:[]}]
},{
val:'c',
children:[{val:'f',children:[]}, {val:'g',children:[]}]
}]
}
// 递归深度遍历
function test(tree) {
console.log(tree.val)
tree.children.forEach(item => {
test(item)
});
}
test(tree) // a-b-d-e-c-f-g
})()依靠树组foreach遍历的顺序,进入哪层打印哪层,同级的会在数组后面,因此从上到下,从左到右
广度优先遍历- 队列(节点出队的同时入队子节点)-队列
for循环进数据,出队的时候输出当前节点并入队子级
用一个队列循环while,类似事件队列的循环,数组有值就自动循环,自动入队,不停执行
(()=>{
const tree ={
val:'a',
children:[{
val:'b',
children:[{val:'d',children:[]}, {val:'e',children:[]}]
},{
val:'c',
children:[{val:'f',children:[]}, {val:'g',children:[]}]
}]
}
// 队列深度遍历
function test(tree) {
const queue = [tree]
while(queue.length) {
// 队列循环(类似事件队列的循环,数组有值就自动循环自动入队)
const item = queue.shift();
console.log(item.val) // 输出当前节点
item.children.forEach(element => {
queue.push(element)
});
}
}
test(tree) // a-b-c-d-e-f-g
})()二叉树
每个节点只有两个或更少节点
数据结构子级不是数组,是具体的属性如 { val:", left:{}, right:{} }
遍历方式
- 深度遍历
- 先序遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 广度遍历
二分搜索树 binary search tree
二分搜索树每个节点的值都比他的左子树的值大,比右子树的值小 属于二叉树结构,因此遍历方式相同,只是数据结构有特殊的规则
很适合于数据搜索 如👇 当需要查找 6 的时候 因为需要查找的值比根节点的值大,所以只需要在根节点的右子树上寻找 大大提高了搜索效率
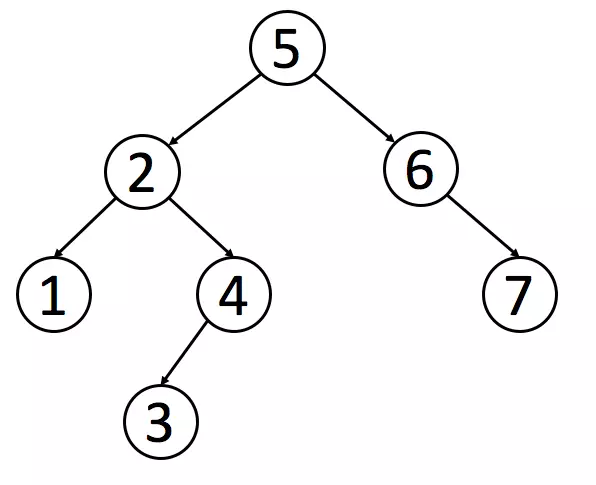
👇 重点在于实现这种数据结构的生成,添加节点
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
}
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null
this.size = 0
}
getSize() {
return this.size
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size === 0
}
addNode(v) {
this.root = this._addChild(this.root, v)
}
// 添加节点时,需要比较添加的节点值和当前
// 节点值的大小
_addChild(node, v) {
if (!node) {
this.size++
return new Node(v)
}
if (node.value > v) {
node.left = this._addChild(node.left, v)
} else if (node.value < v) {
node.right = this._addChild(node.right, v)
}
return node
}
}👇 基于二分搜索树结构数据,遍历先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历 区别在于何时访问节点 每个节点都会遍历三次,分别是遍历到值,遍历左子树和遍历右子树 如 先序遍历,那么只需要第一次遍历到节点时进行操作即可
👇 先序遍历
// 先序遍历可用于打印树的结构
// 先序遍历先访问根节点,然后访问左节点,最后访问右节点。
preTraversal() {
this._pre(this.root)
}
_pre(node) {
if (node) {
console.log(node.value)
this._pre(node.left)
this._pre(node.right)
}
}👇 中序遍历
// 中序遍历可用于排序
// 对于 BST 来说,中序遍历可以实现一次遍历就
// 得到有序的值
// 中序遍历表示先访问左节点,然后访问根节点,最后访问右节点。
midTraversal() {
this._mid(this.root)
}
_mid(node) {
if (node) {
this._mid(node.left)
console.log(node.value)
this._mid(node.right)
}
}👇 后序遍历
// 后序遍历可用于先操作子节点
// 再操作父节点的场景
// 后序遍历表示先访问左节点,然后访问右节点,最后访问根节点。
backTraversal() {
this._back(this.root)
}
_back(node) {
if (node) {
this._back(node.left)
this._back(node.right)
console.log(node.value)
}
}👇 广度遍历(队列
breadthTraversal() {
if (!this.root) return null
let q = new Queue()
// 将根节点入队
q.enQueue(this.root)
// 循环判断队列是否为空,为空
// 代表树遍历完毕
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// 将队首出队,判断是否有左右子树
// 有的话,就先左后右入队
let n = q.deQueue()
console.log(n.value)
if (n.left) q.enQueue(n.left)
if (n.right) q.enQueue(n.right)
}
}二分搜索树-寻找最大/小值
二分搜索树,最小值一定在根节点的最左边,最大值相反
gettMin() {
return this._getMin(this.root).value
}
_getMin(node) {
if (!node.left) return node
return this._getMin(node.left)
}
getMax() {
return this._getMax(this.root).value
}
_getMax(node) {
if (!node.right) return node
return this._getMin(node.right)
}二分搜索树-向上/下取整
向下取整,根据二分搜索树的特性,值一定在根节点的左侧 只需要一直遍历左子树直到当前节点的值不再大于等于需要的值 然后判断节点是否还拥有右子树。有则,继续上面的递归判断
floor(v) {
let node = this._floor(this.root, v)
return node ? node.value : null
}
_floor(node, v) {
if (!node) return null
if (node.value === v) return v
// 如果当前节点值还比需要的值大,就继续递归
if (node.value > v) {
return this._floor(node.left, v)
}
// 判断当前节点是否拥有右子树
let right = this._floor(node.right, v)
if (right) return right
return node
}二分搜索树-排名
🤔 排名和排序不同?
- 获取给定值的排名
- 获取指定排名的节点值
👇 获取指定排名的节点值,让每个节点除了有value、left、right,还拥有一个 size 属性 该属性表示该节点下有多少子节点(包含自身)
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
// 修改代码
this.size = 1
}
}
// 新增代码
_getSize(node) {
return node ? node.size : 0
}
_addChild(node, v) {
if (!node) {
return new Node(v)
}
if (node.value > v) {
// 修改代码
node.size++
node.left = this._addChild(node.left, v)
} else if (node.value < v) {
// 修改代码
node.size++
node.right = this._addChild(node.right, v)
}
return node
}
select(k) {
let node = this._select(this.root, k)
return node ? node.value : null
}
_select(node, k) {
if (!node) return null
// 先获取左子树下有几个节点
let size = node.left ? node.left.size : 0
// 判断 size 是否大于 k
// 如果大于 k,代表所需要的节点在左节点
if (size > k) return this._select(node.left, k)
// 如果小于 k,代表所需要的节点在右节点
// 注意这里需要重新计算 k,减去根节点除了右子树的节点数量
if (size < k) return this._select(node.right, k - size - 1)
return node
}二分搜索树-删除节点
最难实现
- 需要删除的节点没有子树
- 需要删除的节点只有一条子树
- 需要删除的节点有左右两条树
👇 删除最小节点(需要删除的节点没有子树?)
delectMin() {
this.root = this._delectMin(this.root)
console.log(this.root)
}
_delectMin(node) {
// 一直递归左子树
// 如果左子树为空,就判断节点是否拥有右子树
// 有右子树的话就把需要删除的节点替换为右子树
if ((node != null) & !node.left) return node.right
node.left = this._delectMin(node.left)
// 最后需要重新维护下节点的 `size`
node.size = this._getSize(node.left) + this._getSize(node.right) + 1
return node
}👇 删除任意节点
需要取出当前节点的后继节点(也就是当前节点右子树的最小节点)来替换需要删除的节点 然后将需要删除节点的左子树赋值给后继结点,右子树删除后继结点后赋值给他
因为父节点一定比所有左子节点大,比所有右子节点小 当需要删除父节点时,势必需要拿出一个比父节点大的节点来替换父节点 这个节点肯定不存在于左子树,必然存在于右子树 然后又需要保持父节点都是比右子节点小的,那么就可以取出右子树中最小的那个节点来替换父节点
delect(v) {
this.root = this._delect(this.root, v)
}
_delect(node, v) {
if (!node) return null
// 寻找的节点比当前节点小,去左子树找
if (node.value < v) {
node.right = this._delect(node.right, v)
} else if (node.value > v) {
// 寻找的节点比当前节点大,去右子树找
node.left = this._delect(node.left, v)
} else {
// 进入这个条件说明已经找到节点
// 先判断节点是否拥有拥有左右子树中的一个
// 是的话,将子树返回出去,这里和 `_delectMin` 的操作一样
if (!node.left) return node.right
if (!node.right) return node.left
// 进入这里,代表节点拥有左右子树
// 先取出当前节点的后继结点,也就是取当前节点右子树的最小值
let min = this._getMin(node.right)
// 取出最小值后,删除最小值
// 然后把删除节点后的子树赋值给最小值节点
min.right = this._delectMin(node.right)
// 左子树不动
min.left = node.left
node = min
}
// 维护 size
node.size = this._getSize(node.left) + this._getSize(node.right) + 1
return node
}先序遍历(深度优先递归)
根节点-左子树-右子树
(()=>{
const tree ={
val:'1',
left:{
val:'2',
left:{val:'4',left:{},right:{}},
right:{val:'5',left:{},right:{val:'6',left:{},right:{}}}
},
right:{
val:'3',
left:{val:'7',left:{},right:{}},
right:{val:'8',left:{},right:{}}
}
}
// 队列深度遍历
function test(tree) {
if(tree&&tree.val) {
console.log(tree.val); // 根节点
test(tree.left); // 深度进入左边才会开始右边
test(tree.right);
}
}
test(tree)
})()跟普通的深度遍历类似,不过因为树的结构,普通的子级是数组所以是foreach进入,二叉树的子级是属性项直接进入
中序遍历(深度优先递归)
左子树-根节点-右子树
从下到上,从左到右
test(tree.left);
console.log(tree.val);
test(tree.right);只是执行顺序变了
后序遍历(深度优先递归)
左子树-右节点-根节点
从下到上,从右到左
test(tree.left);
test(tree.right);
console.log(tree.val);只是执行顺序变了
不使用递归实现先中后序遍历
用栈模拟递归
AVL 树
二分搜索树实际在业务中是受到限制的,因为并不是严格的 O(logN) 在极端情况下会退化成链表,比如加入一组升序的数字就会造成这种情况
AVL 树改进了二分搜索树,在 AVL 树中任意节点的左右子树的高度差都不大于 1,这样保证了时间复杂度是严格的 O(logN) 因此,对 AVL 树增加或删除节点时可能需要旋转树来达到高度的平衡
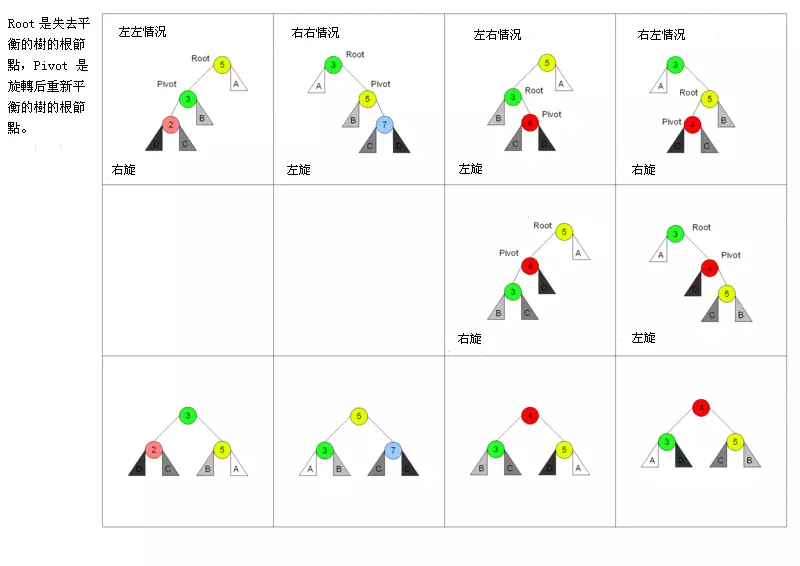
左左情况,新增加的节点位于节点 2 的左侧 这时树已经不平衡,需要旋转 旋转以后也要实现节点比左节点大,比右节点小
旋转之前:new < 2 < C < 3 < B < 5 < A 右旋之后,节点 3 为根节点,这时候需要将节点 3 的右节点加到节点 5 的左边,最后还需要更新节点的高度。
右右 则 相反于左左情况
左右,新增加的节点位于节点 4 的右侧 需要通过两次旋转来达到目的 对节点的左节点左旋,这时树满足左左的情况,再对节点进行一次右旋就可以达到目的
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
this.height = 1
}
}
class AVL {
constructor() {
this.root = null
}
addNode(v) {
this.root = this._addChild(this.root, v)
}
_addChild(node, v) {
if (!node) {
return new Node(v)
}
if (node.value > v) {
node.left = this._addChild(node.left, v)
} else if (node.value < v) {
node.right = this._addChild(node.right, v)
} else {
node.value = v
}
node.height =
1 + Math.max(this._getHeight(node.left), this._getHeight(node.right))
let factor = this._getBalanceFactor(node)
// 当需要右旋时,根节点的左树一定比右树高度高
if (factor > 1 && this._getBalanceFactor(node.left) >= 0) {
return this._rightRotate(node)
}
// 当需要左旋时,根节点的左树一定比右树高度矮
if (factor < -1 && this._getBalanceFactor(node.right) <= 0) {
return this._leftRotate(node)
}
// 左右情况
// 节点的左树比右树高,且节点的左树的右树比节点的左树的左树高
if (factor > 1 && this._getBalanceFactor(node.left) < 0) {
node.left = this._leftRotate(node.left)
return this._rightRotate(node)
}
// 右左情况
// 节点的左树比右树矮,且节点的右树的右树比节点的右树的左树矮
if (factor < -1 && this._getBalanceFactor(node.right) > 0) {
node.right = this._rightRotate(node.right)
return this._leftRotate(node)
}
return node
}
_getHeight(node) {
if (!node) return 0
return node.height
}
_getBalanceFactor(node) {
return this._getHeight(node.left) - this._getHeight(node.right)
}
// 节点右旋
// 5 2
// / \ / \
// 2 6 ==> 1 5
// / \ / / \
// 1 3 new 3 6
// /
// new
_rightRotate(node) {
// 旋转后新根节点
let newRoot = node.left
// 需要移动的节点
let moveNode = newRoot.right
// 节点 2 的右节点改为节点 5
newRoot.right = node
// 节点 5 左节点改为节点 3
node.left = moveNode
// 更新树的高度
node.height =
1 + Math.max(this._getHeight(node.left), this._getHeight(node.right))
newRoot.height =
1 +
Math.max(this._getHeight(newRoot.left), this._getHeight(newRoot.right))
return newRoot
}
// 节点左旋
// 4 6
// / \ / \
// 2 6 ==> 4 7
// / \ / \ \
// 5 7 2 5 new
// \
// new
_leftRotate(node) {
// 旋转后新根节点
let newRoot = node.right
// 需要移动的节点
let moveNode = newRoot.left
// 节点 6 的左节点改为节点 4
newRoot.left = node
// 节点 4 右节点改为节点 5
node.right = moveNode
// 更新树的高度
node.height =
1 + Math.max(this._getHeight(node.left), this._getHeight(node.right))
newRoot.height =
1 +
Math.max(this._getHeight(newRoot.left), this._getHeight(newRoot.right))
return newRoot
}
}Trie 树 (前缀树/字典树)
有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。
为了方便搜索字符串,特点:
- 根节点代表空字符串,每个节点都有 N(假如搜索英文字符,就有 26 条) 条链接,每条链接代表一个字符
- 节点不存储字符,只有路径才存储,这点和其他的树结构不同
- 从根节点开始到任意一个节点,将沿途经过的字符连接起来就是该节点对应的字符串
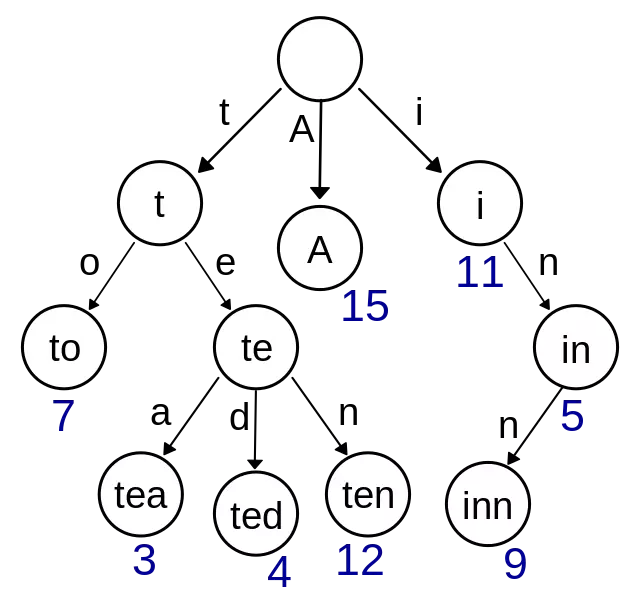
👇 搜索英文字符为例
lass TrieNode {
constructor() {
// 代表每个字符经过节点的次数
this.path = 0
// 代表到该节点的字符串有几个
this.end = 0
// 链接
this.next = new Array(26).fill(null)
}
}
class Trie {
constructor() {
// 根节点,代表空字符
this.root = new TrieNode()
}
// 插入字符串
insert(str) {
if (!str) return
let node = this.root
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
// 获得字符先对应的索引
let index = str[i].charCodeAt() - 'a'.charCodeAt()
// 如果索引对应没有值,就创建
if (!node.next[index]) {
node.next[index] = new TrieNode()
}
node.path += 1
node = node.next[index]
}
node.end += 1
}
// 搜索字符串出现的次数
search(str) {
if (!str) return
let node = this.root
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
let index = str[i].charCodeAt() - 'a'.charCodeAt()
// 如果索引对应没有值,代表没有需要搜素的字符串
if (!node.next[index]) {
return 0
}
node = node.next[index]
}
return node.end
}
// 删除字符串
delete(str) {
if (!this.search(str)) return
let node = this.root
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
let index = str[i].charCodeAt() - 'a'.charCodeAt()
// 如果索引对应的节点的 Path 为 0,代表经过该节点的字符串
// 已经一个,直接删除即可
if (--node.next[index].path == 0) {
node.next[index] = null
return
}
node = node.next[index]
}
node.end -= 1
}
}并查集 (树)
用于处理一些不交集的合并及查询问题
每个节点都有一个父节点,如果只有当前一个节点,那么该节点的父节点指向自己
不是用于遍历
- Find:确定元素属于哪一个子集。它可以被用来确定两个元素是否属于同一子集。
- Union:将两个子集合并成同一个集合。
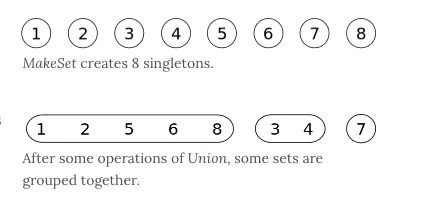
class DisjointSet {
// 初始化样本
constructor(count) {
// 初始化时,每个节点的父节点都是自己
this.parent = new Array(count)
// 用于记录树的深度,优化搜索复杂度
this.rank = new Array(count)
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
this.parent[i] = i
this.rank[i] = 1
}
}
find(p) {
// 寻找当前节点的父节点是否为自己,不是的话表示还没找到
// 开始进行路径压缩优化
// 假设当前节点父节点为 A
// 将当前节点挂载到 A 节点的父节点上,达到压缩深度的目的
while (p != this.parent[p]) {
this.parent[p] = this.parent[this.parent[p]]
p = this.parent[p]
}
return p
}
isConnected(p, q) {
return this.find(p) === this.find(q)
}
// 合并
union(p, q) {
// 找到两个数字的父节点
let i = this.find(p)
let j = this.find(q)
if (i === j) return
// 判断两棵树的深度,深度小的加到深度大的树下面
// 如果两棵树深度相等,那就无所谓怎么加
if (this.rank[i] < this.rank[j]) {
this.parent[i] = j
} else if (this.rank[i] > this.rank[j]) {
this.parent[j] = i
} else {
this.parent[i] = j
this.rank[j] += 1
}
}
}图
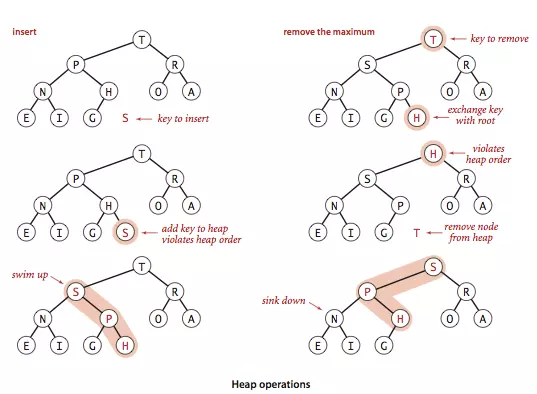
堆
堆通常是一个可以被看做一棵树的数组对象
- 任意节点小于(或大于)它的所有子节点
- 堆总是一棵完全树。即除了最底层,其他层的节点都被元素填满,且最底层从左到右填入。
根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆 根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆
优先队列?也完全可以用堆来实现,操作是一模一样的
实现大根堆
堆的每个节点的左边子节点索引是 i * 2 + 1,右边是 i * 2 + 2,父节点是 (i - 1) /2。
堆有两个核心的操作,分别是 shiftUp 和 shiftDown 。前者用于添加元素,后者用于删除根节点。
shiftUp 的核心思路是一路将节点与父节点对比大小,如果比父节点大,就和父节点交换位置。
shiftDown 的核心思路是先将根节点和末尾交换位置,然后移除末尾元素。接下来循环判断父节点和两个子节点的大小,如果子节点大,就把最大的子节点和父节点交换。
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = []
}
size() {
return this.heap.length
}
empty() {
return this.size() == 0
}
add(item) {
this.heap.push(item)
this._shiftUp(this.size() - 1)
}
removeMax() {
this._shiftDown(0)
}
getParentIndex(k) {
return parseInt((k - 1) / 2)
}
getLeftIndex(k) {
return k * 2 + 1
}
_shiftUp(k) {
// 如果当前节点比父节点大,就交换
while (this.heap[k] > this.heap[this.getParentIndex(k)]) {
this._swap(k, this.getParentIndex(k))
// 将索引变成父节点
k = this.getParentIndex(k)
}
}
_shiftDown(k) {
// 交换首位并删除末尾
this._swap(k, this.size() - 1)
this.heap.splice(this.size() - 1, 1)
// 判断节点是否有左孩子,因为二叉堆的特性,有右必有左
while (this.getLeftIndex(k) < this.size()) {
let j = this.getLeftIndex(k)
// 判断是否有右孩子,并且右孩子是否大于左孩子
if (j + 1 < this.size() && this.heap[j + 1] > this.heap[j]) j++
// 判断父节点是否已经比子节点都大
if (this.heap[k] >= this.heap[j]) break
this._swap(k, j)
k = j
}
}
_swap(left, right) {
let rightValue = this.heap[right]
this.heap[right] = this.heap[left]
this.heap[left] = rightValue
}
}集合
没有重复项
刚好 ES6的 Set:无序、唯一的
集合的常用操作 去重、判断是否在集合里、求两个集合的交集
// 去重
const arr = [1,1,2,2]
const newArr = [...new Set(arr)];
// 判断是否在集合里
[new Set(arr)].has(1)
// 两个集合的交集 遍历其中一个集合每一项判断是否在另一个集合里面
const arr1 = new Set([2,3,4,5])
const arr2 = new Set([1,2,3,4])
const arr3 = new Set([...arr1].filter(item=> arr2.has(item)))👆 集合就是普通的数据堆(对象、数组),只不过过滤了一次重复项而已 同字典数据结构的2个数组的交集
总结
栈、队列、链表 讲究先后进出,讲究指针next 证明这些都是有序的数据结构 另外这些都是可以有重复项的